Metallography Testing
We have extensive experience across a wide range of industries
Metallurgical Testing of Metallic Materials


Metallurgical Testing is carried out to study the microstructural and macrostructural characteristics of metallic materials. These tests provide critical insights into a material’s internal structure, processing quality, heat treatment effects, and overall suitability for intended applications.
This analysis helps to:
- Evaluate the effects of manufacturing processes, heat treatments, and welding on material structure
- Detect defects such as cracks, segregation, porosity, decarburization, or improper grain structure
- Ensure compliance with relevant standards and customer specifications
- Support failure analysis, quality control, and material development studies
At MIC Labs, metallurgical examinations are performed using advanced microscopy and metallography equipment:
- Stereo Zoom Microscope (0.5x – 4.5x magnification): For macrostructural evaluation and surface feature inspection
- Inverted Metallurgical Microscope (50x – 1000x magnification): For detailed microstructural analysis and metallographic investigations
Metallurgical Tests Conducted at MIC Labs:
- Macrostructure Examination
- Microstructure Examination
- Average Grain Size Measurement
- Metal and Oxide Coating Thickness Measurement
- Determination of Non-Metallic Inclusions
- Case Depth Measurement in Steels
- Measurement of Depth of Decarburization
- Visual Evaluation of Graphite in Cast Irons
- Phase Analysis (Delta Ferrite Determination)
- Susceptibility to Intergranular Corrosion (Method A & E)
Applications & Benefits:
- Quality control in steel, aluminium, copper, nickel, and other metallic materials
- Material verification and defect detection for production and fabrication industries
- R&D and failure analysis to improve material performance
- Compliance assurance with international and customer-specific standards
MIC Labs provides metallurgical testing services across India, including Hyderabad, Bangalore, Mumbai, Delhi, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Ahmedabad, Gurugram, Noida, and other major industrial hubs.
Macro Structure Examination of Metallic Materials
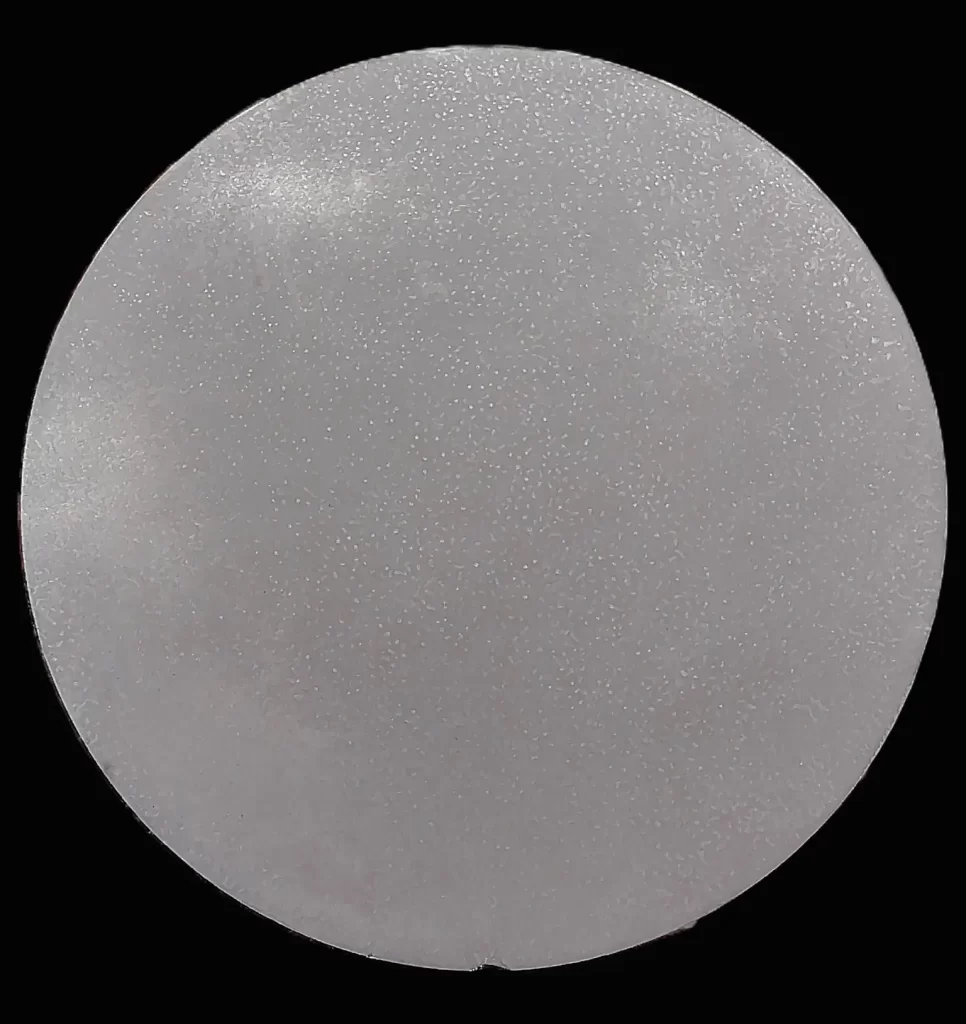

Macrostructural Examination involves observing the overall structure of a metallic component at low magnification. The surface is carefully polished and etched to reveal key features such as weld zones, grain flow, segregation, porosity, cracks, and other visible defects.
This test is essential for assessing the quality and integrity of castings, forgings, welds, and rolled products. It is widely used in manufacturing quality checks, failure investigations, and material acceptance tests, ensuring large-scale structural integrity of metallic components.
Applications & Benefits:
- Quality assurance for castings, forgings, and rolled metals
- Detection of defects such as cracks, porosity, or improper grain flow
- Support for failure analysis and material validation
- Verification of manufacturing processes and weld quality
Testing Standards:
ASTM E340 | ASTM E381
Microstructure Examination of Metallic Materials
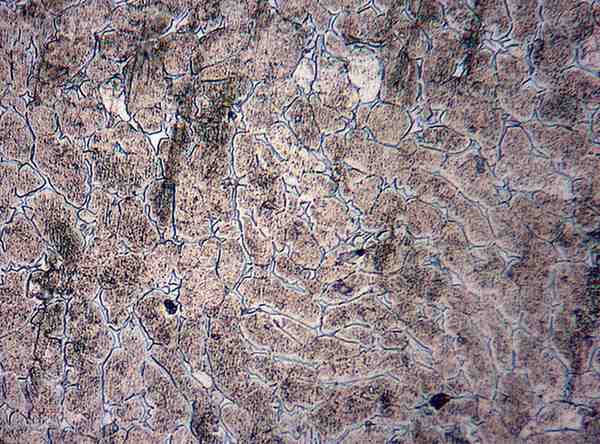
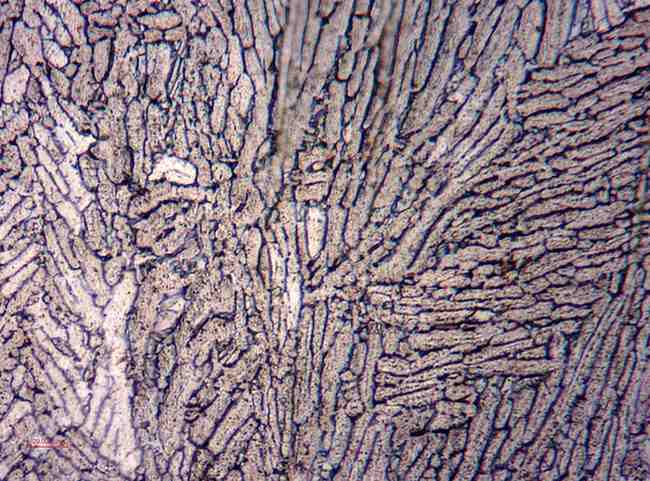
Microstructural Analysis involves studying the internal structure of metals at high magnification. Using polishing and etching metallographic techniques, this test reveals phases, grain boundaries, inclusions, precipitates, and the effects of heat treatment on the material.
Microstructure plays a critical role in determining mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, hardness, and overall material performance. This examination is essential for process verification, quality assurance, and failure analysis, helping detect potential weaknesses or deviations from specifications before product deployment.
Applications & Benefits:
- Material quality assurance in steel, aluminium, copper, nickel, and other alloys
- Detection of microstructural defects such as inclusions or improper grain formation
- Support for R&D and metallurgical studies
- Verification of heat treatment and manufacturing processes
Reference Standard:
ASM Volume – 9
Average Grain Size Measurement of Metallic Materials
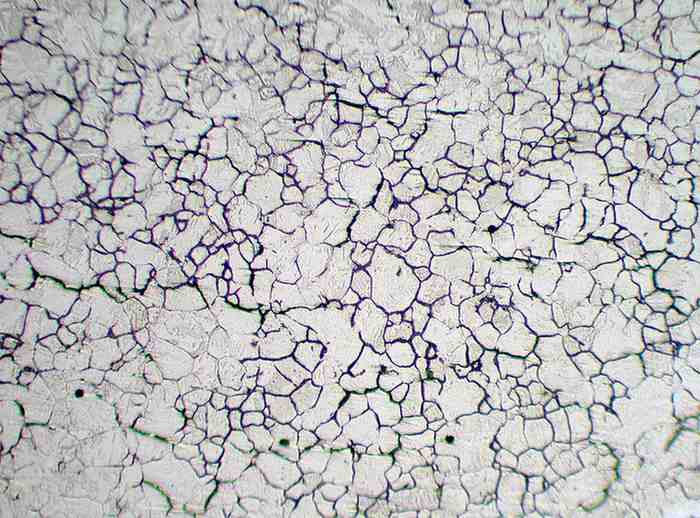
Grain Size Measurement evaluates the size and distribution of metallic grains within a material, typically using microscopic comparison methods or image analysis. Grain size directly influences how metals deform under stress and respond to heat treatment, impacting their mechanical properties.
Smaller grains generally improve strength, toughness, and durability, making this test critical for steels, alloys, and other high-performance components. It ensures materials meet design specifications and mechanical property requirements for reliable performance.
Applications & Benefits:
- Quality control for steels, aluminium, copper, nickel, and other alloys
- Verification of heat treatment effects and manufacturing processes
- Support for R&D and failure analysis
- Ensures compliance with design and material standards
Testing Standards:
ASTM E112 | IS 4748
Metal and Oxide Coating Thickness Measurement
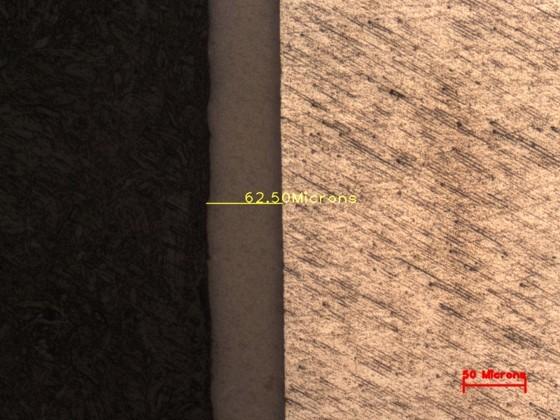
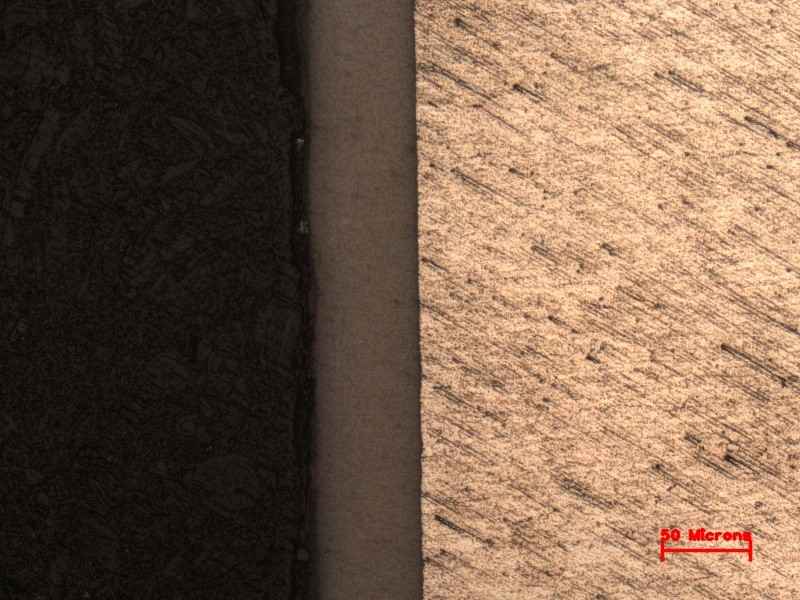
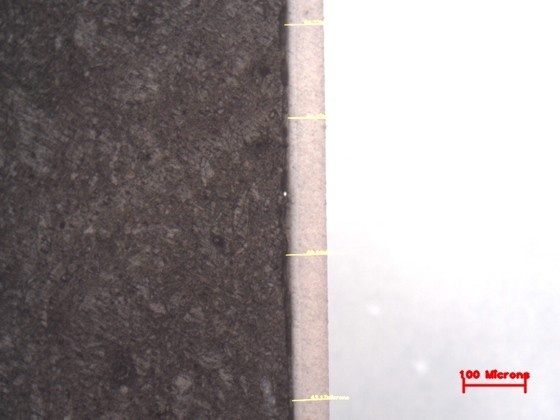


Metal and Oxide Coating Thickness Measurement determines the thickness of surface coatings, including metal platings, anodized layers, or naturally formed oxides. Samples are prepared for cross-sectional microscopic analysis to precisely measure the coating thickness.
This test ensures uniformity and effectiveness of coatings, providing corrosion protection, wear resistance, and durability. It is widely applied to electroplated parts, protective coatings on automotive and aerospace components, and corrosion-resistant metals.
Applications & Benefits:
- Quality assurance for electroplated, anodized, and coated components
- Verification of corrosion protection and wear resistance
- Inspection of automotive, aerospace, and industrial parts
- Support for R&D and material development studies
Testing Standards:
ASTM B487 | ISO 1463 | IS 3203
Determination of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Metallic Materials
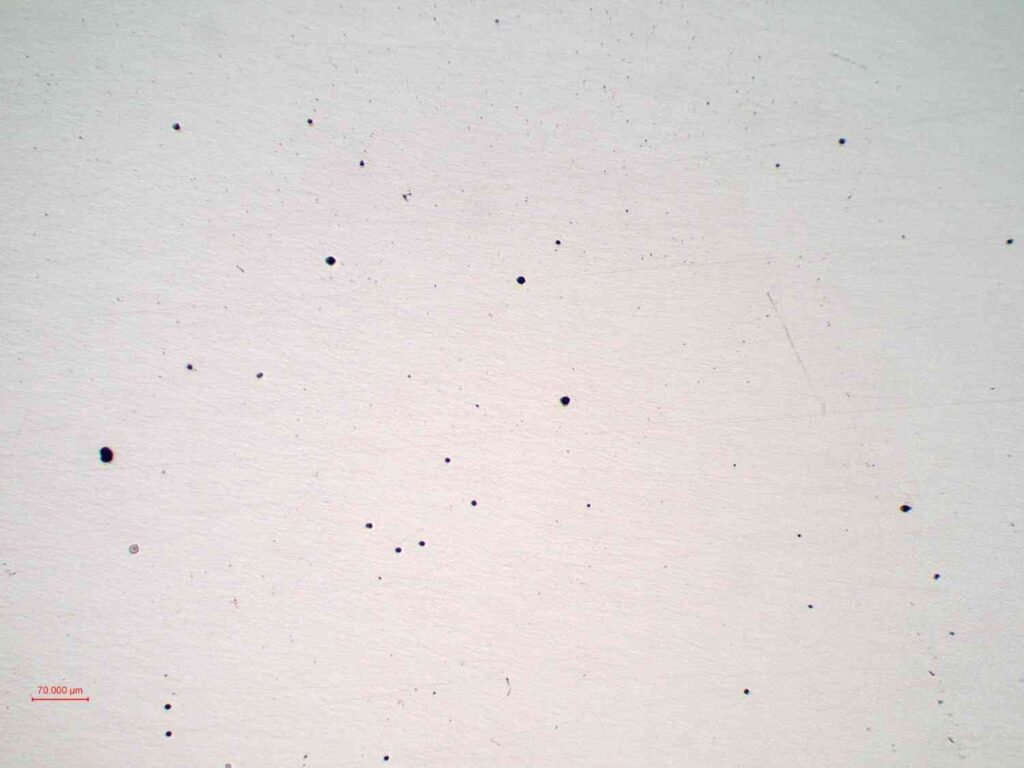

Non-Metallic Inclusions Analysis identifies oxides, sulfides, silicates, and other inclusions that form during melting or processing of metals. Using microscopic metallurgical analysis, this test evaluates the type, size, and quantity of inclusions in steel and alloy samples.
High inclusion content can reduce toughness, ductility, and fatigue resistance, making this test critical for high-strength steels, bearing steels, and components exposed to cyclic or high-stress applications. It ensures that materials meet stringent mechanical and performance standards.
Applications & Benefits:
- Quality control of steels and alloys for high-performance applications
- Detection of microstructural defects affecting fatigue and toughness
- Support for R&D and failure analysis
- Verification of manufacturing and heat treatment processes
Testing Standards:
ASTM E45 | IS 4163
Case Depth Measurement of Steels
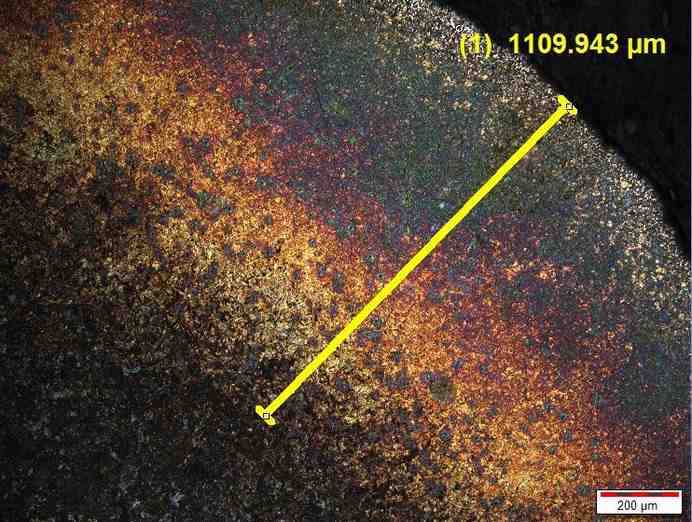


Case Depth Measurement determines the thickness of hardened layers created by surface hardening processes such as carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening. Samples are prepared metallographically and examined under a microscope to accurately measure the hardened layer depth.
This test ensures that gears, shafts, bearings, and other critical components have sufficient surface hardness for wear resistance while maintaining a tough and durable core for structural support. It is essential for quality assurance, performance verification, and failure prevention in engineering components.
Applications & Benefits:
- Verification of surface hardening processes for gears, shafts, and bearings
- Quality control for automotive, aerospace, and industrial components
- Support for R&D and metallurgical studies
- Ensures compliance with design and material standards
Testing Standard:
IS 6416
MIC Labs provides metallurgical testing services across India, including Hyderabad, Bangalore, Mumbai, Delhi, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Ahmedabad, Gurugram, Noida, and other major industrial hubs.
Depth of Decarburization Measurement

Decarburization is the loss of carbon near the surface of steel during heat treatment or exposure to oxidizing environments. This test determines the depth of the softened or decarburized layer through microscopic metallographic examination.
Measuring the depth of decarburization is essential to prevent a reduction in surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. It is especially critical for structural components, automotive parts, and high-performance steels, where surface integrity directly affects durability and service life.
Applications & Benefits:
Quality control for heat-treated and surface-hardened steels
Prevention of strength and wear loss in critical components
Verification of manufacturing and heat treatment processes
Support for metallurgical and failure analysis
Testing Standards:
ASTM E1077 | IS 6396
Visual Evaluation of Graphite in Cast Iron

Graphite Evaluation in Cast Iron involves examining graphite size, shape, distribution, and amount under a microscope, both before and after etching. Cast irons contain graphite in flake, nodular, or temper form, and this morphology directly affects their mechanical properties.
The shape and distribution of graphite influence strength, ductility, and machinability, making this test vital for classifying cast iron grades such as grey, ductile, and malleable iron. It ensures materials meet IS and ASTM standards for consistent quality and performance.
Applications & Benefits:
- Classification of cast iron grades (grey, ductile, malleable)
- Quality control in foundries and casting industries
- Assessment of mechanical properties through graphite morphology
- Support for R&D and metallurgical analysis
Testing Standards:
ASTM A247 | IS 7754
Phase Analysis (Delta Ferrite Determination)
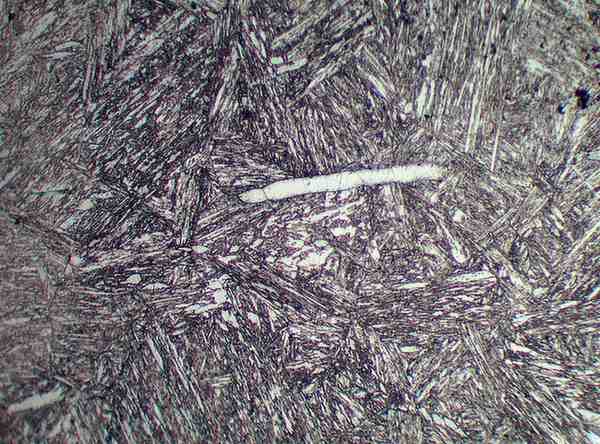
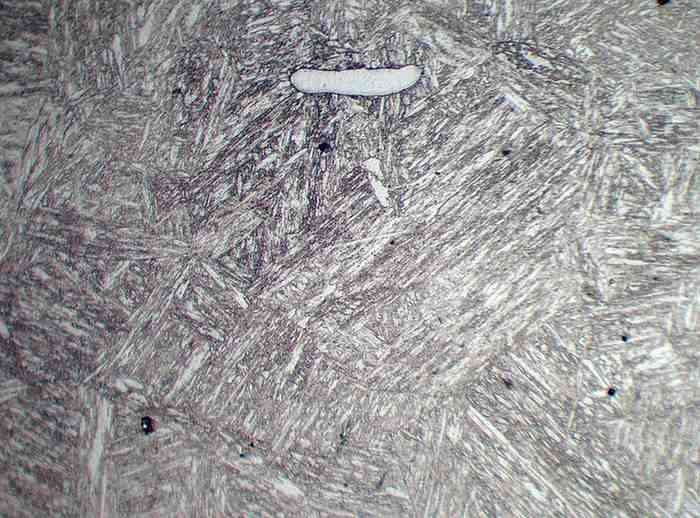
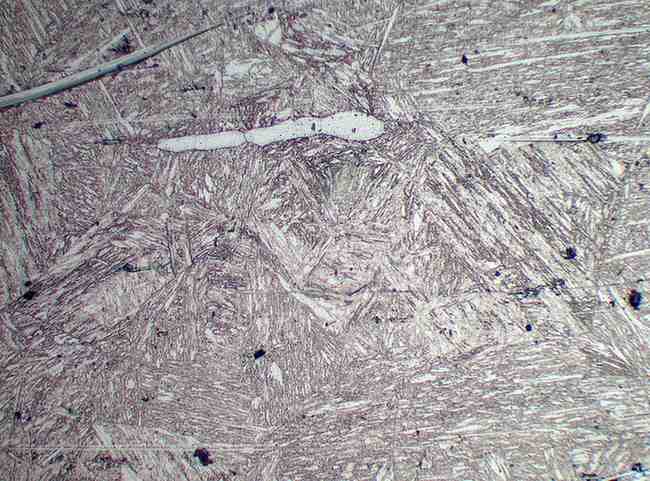
Phase Analysis determines the presence and quantity of delta ferrite in stainless steels and welds using advanced metallographic examination. Delta ferrite plays a vital role in improving toughness and reducing hot cracking susceptibility in austenitic stainless steels.
This test is essential for evaluating corrosion resistance, weld integrity, and mechanical performance in components exposed to high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments such as chemical plants, petrochemical equipment, marine structures, and pressure vessels.
Applications & Benefits:
- Determination of delta ferrite content in stainless steel welds and components
- Verification of corrosion resistance and weld quality
- Support for process validation and material selection
- Ensures compliance with industry standards and specifications
Testing Standards:
ASTM E562 | AMS 2315H
Susceptibility to Intergranular Corrosion (Method A & E)

Intergranular Corrosion (IGC) Testing evaluates the resistance of stainless steels to corrosion that occurs along grain boundaries due to improper heat treatment or sensitization.
- Method A serves as a rapid screening test,
- Method E provides a detailed and standardized evaluation of corrosion behavior.
This test is essential for ensuring long-term durability, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity of stainless steels used in chemical processing, power generation, marine environments, and high-temperature service applications.
Applications & Benefits:
- Assessment of corrosion susceptibility in stainless steels and welds
- Verification of proper heat treatment and sensitization control
- Quality assurance for critical components and process equipment
- Compliance with ASTM and international standards
Testing Standard:
ASTM A262
Metallography Testing Sample Preparation – FAQs
1. Why is sample preparation important in metallography testing?
Proper sample preparation ensures accurate microstructural analysis by removing surface irregularities, minimizing distortions, and enhancing visibility under a microscope. It helps in identifying grain structure, phases, inclusions, and defects without interference.
2. What are the key steps in metallography sample preparation?
The process includes sectioning (cutting the sample), mounting (embedding in resin/epoxy), grinding (smoothing the surface), polishing (achieving a mirror-like finish), and etching (revealing microstructural details using chemical reagents). Each step is essential to obtaining clear and reliable results.
3. What materials require metallographic sample preparation?
Metallography is used for metals, alloys, ceramics, and composite materials in industries like aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, and defense to assess material properties and quality.
4. What types of microscopes are used for metallography testing?
Metallographic analysis is performed using optical microscopes, scanning electron microscopes (SEM), and digital image analysis systems to examine microstructures at different magnifications and detail levels.
5. How does etching help in metallography testing?
Etching uses chemical solutions to reveal features like grain boundaries, phase distributions, and defects that are not visible in the polished state. The type of etchant depends on the material being tested and the specific microstructural details needed.
Looking for Metallurgical testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
Metallography Testing Process

Metallography testing is a crucial process for examining the microstructure of metals and alloys, helping to assess grain structure, phase distribution, and potential defects. The process begins with selecting a representative sample that accurately reflects the material’s properties. This is followed by sectioning, where precision cutting techniques minimize thermal damage and distortion. Next, the sample is mounted in resin or epoxy to provide stability during further preparation. Grinding and polishing then refine the surface using abrasive materials, ensuring a smooth, mirror-like finish for accurate analysis. To reveal structural details, the sample undergoes etching with a chemical solution that highlights grain boundaries and phase differences. Finally, microscopic examination using optical or electron microscopes provides a detailed view of the material’s microstructure. This well-structured process ensures reliable and repeatable results, making metallography testing essential for quality control, failure analysis, and material development in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.















Metallography Testing Process – FAQs
1. What is metallography testing?
Metallography testing is the study of a material’s microstructure through cutting, mounting, grinding, polishing, etching, and microscopic examination to assess grain structure, phase distribution, and defects.
2. Why is sample preparation important in metallography?
Proper sample preparation ensures accurate results by minimizing surface damage, eliminating artifacts, and revealing true microstructural details for precise analysis.
3. What is the purpose of etching in metallography?
Etching uses chemical solutions to highlight grain boundaries, phases, and microstructural features that are not visible in the polished state, making them easier to analyze under a microscope.
4. Which microscopes are used for metallography testing?
Optical microscopes and scanning electron microscopes (SEM) are commonly used, with SEM providing higher magnification and deeper insights into material characteristics.
5. In which industries is metallography testing used?
It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, defense, manufacturing, and research laboratories for quality control, failure analysis, and material development.
Looking for tensile testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
Metallography Testing Sample Preparation


Metallography testing involves the study of a material’s microstructure to evaluate its grain structure, phase distribution, defects, and overall quality. Proper sample preparation is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable results. At MIC Labs, the sample preparation process follows ASTM, ISO, and IS standards, ensuring consistency and precision.
The process begins with sample selection, where a representative portion of the material is chosen. The selected sample is then sectioned using precision cutting techniques to avoid altering the microstructure. After sectioning, the sample undergoes mounting, where it is embedded in a resin or epoxy to facilitate handling and protect the edges during further processing.
The next step is grinding and polishing, where the sample surface is progressively refined using abrasive papers and polishing compounds to achieve a smooth, mirror-like finish. This step is critical to eliminating scratches and distortions that could interfere with microscopic analysis. If required, the sample undergoes etching, where it is treated with chemical reagents to reveal microstructural details like grain boundaries and phase distributions.
Once prepared, the sample is examined under a metallurgical microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), or optical microscope, depending on the testing requirements. This detailed examination helps assess the material’s properties, including grain size, inclusion content, porosity, and heat treatment effects, making metallography essential for quality control, failure analysis, and research in industries like aerospace, automotive, defense, and manufacturing.
Metallography Testing Sample Preparation – FAQs
1. Why is sample preparation important in metallography testing?
Proper sample preparation ensures accurate microstructural analysis by removing surface irregularities, minimizing distortions, and enhancing visibility under a microscope. It helps in identifying grain structure, phases, inclusions, and defects without interference.
2. What are the key steps in metallography sample preparation?
The process includes sectioning (cutting the sample), mounting (embedding in resin/epoxy), grinding (smoothing the surface), polishing (achieving a mirror-like finish), and etching (revealing microstructural details using chemical reagents). Each step is essential to obtaining clear and reliable results.
3. What materials require metallographic sample preparation?
Metallography is used for metals, alloys, ceramics, and composite materials in industries like aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, and defense to assess material properties and quality.
4. What types of microscopes are used for metallography testing?
Metallographic analysis is performed using optical microscopes, scanning electron microscopes (SEM), and digital image analysis systems to examine microstructures at different magnifications and detail levels.
5. How does etching help in metallography testing?
Etching uses chemical solutions to reveal features like grain boundaries, phase distributions, and defects that are not visible in the polished state. The type of etchant depends on the material being tested and the specific microstructural details needed.
Looking for tensile testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
Registration & Certifications
We are a certified and registered organization committed to quality and compliance.

Accredited by NABL
(National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories – India)
Our laboratory is accredited by NABL as it meets international standards for quality and competence.
It operates in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025:2017. NABL accreditation is recognized
both nationally and internationally.
If you are looking for NABL-accredited testing laboratories in India, our facility provides high-precision testing services in compliance with global quality standards
- Tensile Testing: ASTM E8M, ASTM E21, ASTM B557M, ASTM A770, ASTM D3039M, ASTM D412, ASTM D638, IS 1608 (Part-1, Part-3), ISO 6892
- Compression Testing: ASTM D575
- Bend Testing: ASTM E290, IS 1599
- Low Cycle Fatigue Testing: ASTM E606
- High Cycle Fatigue Testing: ASTM E466
- Fatigue Crack Growth Rate Testing: ASTM E647
- Fracture Toughness Testing (KIC): ASTM E399
- Fracture Toughness Testing (JIC): ASTM E1820
- Creep & Stress Rupture Testing: ASTM E139, ASTM E292

AS9100:2016 Certified
MIC Labs is certified by IAS in accordance with AS9100:2016, meeting international aerospace quality standards.

Approved by DGAQA
MIC Labs is approved by DGAQA, ensuring compliance with aerospace and defense testing requirements.

Registered by UDYAM
Measure India Corporation Pvt Ltd is UDYAM registered, recognizing us as a certified MSME in India.
This registration highlights our commitment to quality, statutory compliance, and industry standards.
Why Choose Us
We have 20 years of experience in providing material testing systems and offering testing services with great confidence.
- 90+ Products
- 500+ Customers
- 35+ Team Size
- Expertise in guiding and working with top-notch researchers and engineers
- World-class mechanical testing laboratory
Mechanical Testing Lab Services & Universal Testing Machines Suppliers in India
“With over 20 years of experience, Measure India Corporation Pvt Ltd supplies Universal Testing Machines & mechanical testing services, ensuring precision, reliability, and compliance with ASTM, ISO, and global standards across various industries.”

























Contact Information
9:00 AM – 5:30 PM
Sreenagar, Rampally,
Hyderabad, Telangana 501301
Get In Touch With Us
Please fill out the form below and a member of our team will respond promptly.
