Creep and Stress Rupture Testing services in India
We have extensive experience across a wide range of industries
How Creep and Stress Rupture Testing Works
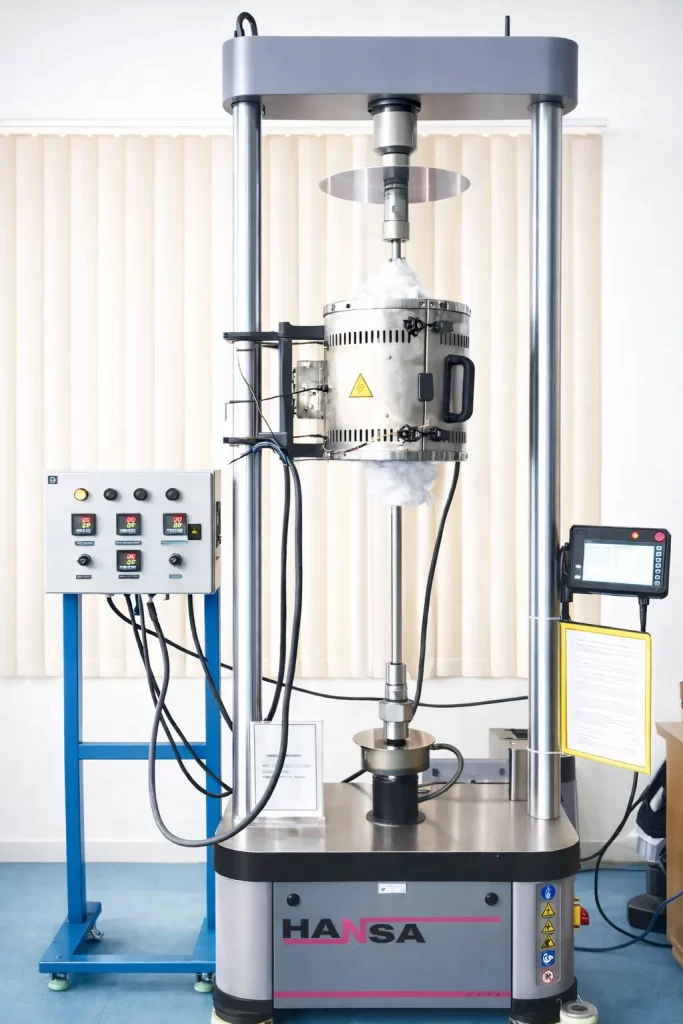

Creep and Stress Rupture Testing evaluates a material’s ability to withstand prolonged stress at elevated temperatures. These tests are essential for industries like aerospace, power generation, automotive, and manufacturing, where materials must perform reliably under extreme conditions over extended periods.
1. ASTM E139 – Standard Test Method for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
Specifies test procedures for measuring creep deformation and rupture life.
Includes guidelines for sample preparation, gripping, and temperature control.
Used for aerospace, power generation, and high-temperature applications.
2. ISO 204 – Metallic Materials – Uniaxial Creep Testing in Tension – Method of Test
Defines creep testing methodology under constant load and elevated temperature.
Specifies requirements for strain measurement and test duration.
Standardized for engineering materials used in high-temperature environments.
3. ASTM E292 – Standard Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture Notch Tension Tests of Materials
Focuses on stress rupture testing, measuring time to failure under sustained load.
Includes notched and unnotched specimen testing for material performance evaluation.
Commonly applied in turbine blades, boilers, and structural components.
4. ISO 7539-5 – Corrosion of Metals and Alloys – Stress Corrosion Testing
Establishes test methods for materials exposed to high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Evaluates the combined effect of stress and environmental conditions on creep rupture behavior.
5. ASTM D2990 – Standard Test Methods for Tensile, Compressive, and Flexural Creep and Creep-Rupture of Plastics
Defines test methods for evaluating creep and stress rupture in plastic materials.
Used for polymeric materials in automotive, aerospace, and structural applications.
These standards ensure that Creep and Stress Rupture Testing follows globally accepted methodologies, providing accurate, reliable, and repeatable results for material selection and durability assessment.

Creep and Stress Rupture Testing – FAQs
1. What is the difference between Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
- Creep Testing measures gradual deformation of a material under constant stress and elevated temperature over time.
- Stress Rupture Testing focuses on determining the time it takes for the material to fail (rupture) under sustained load and high temperature.
2. Why is Creep and Stress Rupture Testing important?
These tests help industries predict material performance and lifespan in high-temperature and high-stress environments, such as aerospace, power plants, and manufacturing. It ensures materials can withstand prolonged stress without unexpected failure.
3. How long does Creep Testing take?
Creep testing can last from a few hours to several months or even years, depending on the material and test conditions. Some critical applications require long-term creep tests to assess material behavior over its expected service life.
4. What are the key factors affecting Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
- Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate creep deformation.
- Applied Load: Increased stress levels lead to faster material failure.
- Material Composition: Different alloys and polymers exhibit varying creep resistance.
- Test Duration: Longer tests provide a clearer understanding of material behavior over time.
5. What standards are followed for Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
Testing follows international standards like:
- ASTM E139 – Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Testing of Metals.
- ISO 204 – Uniaxial Creep Testing of Metallic Materials.
- ASTM E292 – Stress Rupture Testing of Metals.
- ASTM D2990 – Creep and Stress Rupture Testing of Plastics.
These standards ensure accurate, repeatable, and industry-accepted test results for material selection and performance validation.
Looking for Creep and Stress Rupture Testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
Creep and Stress Rupture Testing Gripping Process
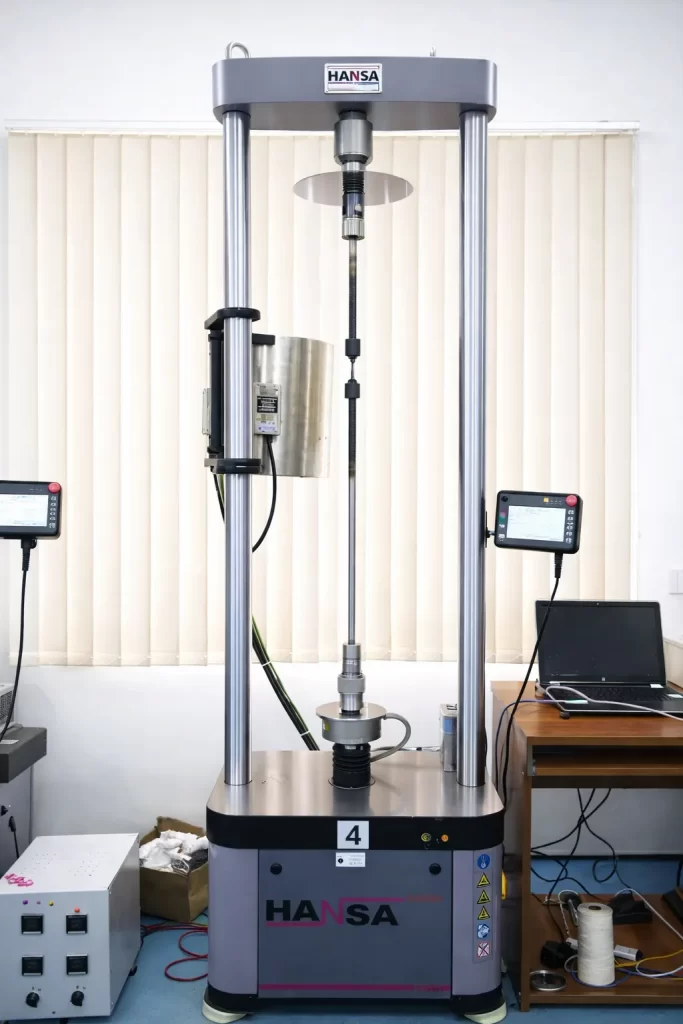

The gripping process is a critical step in Creep and Stress Rupture Testing, ensuring that test specimens are securely held without introducing additional stresses or deformations that could affect test accuracy.















Key Aspects of the Gripping Process
Selection of Grip Type
Threaded Grips – Used for round specimens with threaded ends, ensuring firm engagement.
Pin-Loaded Grips – Used for flat specimens, allowing smooth force transmission.
Shoulder-End Grips – Designed for high-temperature testing to prevent slippage.
Specimen Alignment
Proper axial alignment is ensured to prevent bending stresses.
Misalignment can lead to premature failure or inaccurate data.
Minimizing Stress Concentrations
The gripping region is designed to prevent excessive localized stress.
Precision machining ensures a gradual transition between the gauge length and grip section.
High-Temperature Gripping Considerations
Special grip materials are used to withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Thermal expansion is accounted for to prevent specimen slippage.
Compliance with Testing Standards
Gripping methods comply with ASTM E139 (Creep Testing) and ASTM E292 (Stress Rupture Testing).
MIC Labs follows ISO and IS guidelines to ensure globally recognized accuracy.
With advanced gripping systems, precise specimen preparation, and expert handling, MIC Labs ensures reliable and repeatable Creep and Stress Rupture Testing results.
Creep and Stress Rupture Testing Gripping – FAQs
1. Why is the gripping process important in Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
The gripping process ensures that the specimen is securely held without introducing additional stresses or misalignment, which could affect test accuracy and lead to premature failure. Proper gripping ensures reliable and repeatable test results.
2. What types of grips are used in Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
Common grip types include:
- Threaded Grips – Used for round specimens with threaded ends.
- Pin-Loaded Grips – Ideal for flat specimens to distribute stress evenly.
- Shoulder-End Grips – Designed for high-temperature tests to prevent slippage.
3. How is misalignment prevented during gripping?
Misalignment is prevented by:
- Using precision-machined grips for accurate axial alignment.
- Ensuring a gradual transition between the gauge length and grip section.
- Applying minimal preload force before full test loading.
4. What challenges arise when gripping specimens at high temperatures?
At high temperatures, materials expand and can soften, leading to slippage. To prevent this:
- High-temperature-resistant grips are used.
- Thermal expansion is considered during the setup.
- Special coatings or grip inserts enhance holding strength.
5. What standards govern the gripping process in these tests?
Gripping methods comply with:
- ASTM E139 (Creep Testing)
- ASTM E292 (Stress Rupture Testing)
- ISO and IS standards for industry-wide consistency
By following precise gripping techniques and industry standards, MIC Labs ensures accurate, repeatable, and high-quality Creep and Stress Rupture Testing results.
Looking for tensile testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-Certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
How Creep and Stress Rupture Testing Works – Process & Importance

At MIC Labs, precise sample preparation is the foundation of accurate Creep and Stress Rupture Testing. Our in-house sample preparation workshop, established in 2023, is equipped with state-of-the-art machining centers to ensure high-quality specimens that meet the stringent requirements of ASTM, ISO, and IS standards.
Key Aspects of Sample Preparation:
Material Selection & Extraction
Raw material is carefully selected and extracted with minimal defects.
Ensuring uniformity to maintain consistency in testing results.
Precision Machining & Shaping
Specimens are machined to tight tolerances with controlled dimensions.
CNC machining for uniform gauge sections and accurate cross-sectional areas.
Polishing & Surface Finish
Specimens are polished to remove machining marks and surface irregularities.
Reducing stress concentration points that could impact test results.
Compliance with International Standards
Specimens are prepared following ASTM E139 (Creep Testing) and ASTM E292 (Stress Rupture Testing) guidelines.
Other relevant ISO and IS standards are also adhered to for global reliability.
Custom Specimen Preparation
MIC Labs can prepare specimens for various industries such as aerospace, defense, manufacturing, and power generation.
Tailored specimen geometries based on client requirements.
With expert machinists, high-precision equipment, and strict quality control, MIC Labs ensures that every sample meets the highest standards for Creep and Stress Rupture Testing.
Creep and Stress Rupture Testing Sample Preparation – FAQs
1. What are the key factors in preparing samples for Creep and Stress Rupture Testing?
The key factors include precise machining, dimensional accuracy, uniform gauge sections, surface finishing, and compliance with ASTM, ISO, and IS standards. Proper preparation ensures accurate and repeatable test results.
2. What are the standard dimensions for creep test specimens?
Specimen dimensions vary based on testing standards. Common types include:
- Round specimens (ASTM E139) with gauge lengths of 25mm to 50mm.
- Flat specimens (ASTM E292) with specific thicknesses based on material and application.
3. How does surface finishing impact creep test results?
A smooth, polished surface minimizes stress concentration points and ensures uniform stress distribution, reducing the risk of premature failure due to surface defects.
4. Can MIC Labs prepare custom test specimens based on client requirements?
Yes, MIC Labs provides custom sample preparation tailored to specific industry needs, including aerospace, defense, manufacturing, and power generation applications.
5. What standards does MIC Labs follow for sample preparation?
We adhere to internationally recognized standards such as:
- ASTM E139 (Creep Testing)
- ASTM E292 (Stress Rupture Testing)
- ISO and IS standards as required for industry compliance.
For high-precision and reliable sample preparation, MIC Labs ensures state-of-the-art machining, expert craftsmanship, and strict quality control.
Looking for tensile testing services in India? Get accurate, NABL-certified material testing with advanced Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) today!
Registration & Certifications
We are a certified and registered organization committed to quality and compliance.

Accredited by NABL
(National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories – India)
Our laboratory is accredited by NABL as it meets international standards for quality and competence.
It operates in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025:2017. NABL accreditation is recognized
both nationally and internationally.
If you are looking for NABL-accredited testing laboratories in India, our facility provides high-precision testing services in compliance with global quality standards
- Tensile Testing: ASTM E8M, ASTM E21, ASTM B557M, ASTM A770, ASTM D3039M, ASTM D412, ASTM D638, IS 1608 (Part-1, Part-3), ISO 6892
- Compression Testing: ASTM D575
- Bend Testing: ASTM E290, IS 1599
- Low Cycle Fatigue Testing: ASTM E606
- High Cycle Fatigue Testing: ASTM E466
- Fatigue Crack Growth Rate Testing: ASTM E647
- Fracture Toughness Testing (KIC): ASTM E399
- Fracture Toughness Testing (JIC): ASTM E1820
- Creep & Stress Rupture Testing: ASTM E139, ASTM E292

AS9100:2016 Certified
MIC Labs is certified by IAS in accordance with AS9100:2016, meeting international aerospace quality standards.

Approved by DGAQA
MIC Labs is approved by DGAQA, ensuring compliance with aerospace and defense testing requirements.

Registered by UDYAM
Measure India Corporation Pvt Ltd is UDYAM registered, recognizing us as a certified MSME in India.
This registration highlights our commitment to quality, statutory compliance, and industry standards.
Why Choose Us
We have 20 years of experience in providing material testing systems and offering testing services with great confidence.
- 90+ Products
- 500+ Customers
- 35+ Team Size
- Expertise in guiding and working with top-notch researchers and engineers
- World-class mechanical testing laboratory
Mechanical Testing Lab Services & Universal Testing Machines Suppliers in India
“With over 20 years of experience, Measure India Corporation Pvt Ltd supplies Universal Testing Machines & mechanical testing services, ensuring precision, reliability, and compliance with ASTM, ISO, and global standards across various industries.”





































Contact Information
9:00 AM – 5:30 PM
Sreenagar, Rampally,
Hyderabad, Telangana 501301
Get In Touch With Us
Please fill out the form below and a member of our team will respond promptly.
